CONTROL OF MOS BY ANTIBIOTICS
INHIBITION OF NUCLEIC ACID & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS:

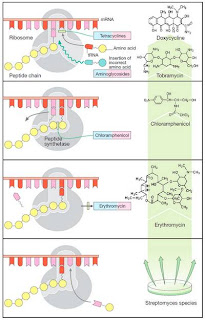
3). Chloramphenicol : Chloramphenicol is considered as pro typical broad spectrum antibiotics alongside tetracycline & is effective against a wide variety of Gram positive & Gram negative bacteria, most anaerobic microorganisms.
Mechanism of Action:
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antibiotic that stops bacterial growth by inhibiting protein synthesis. It prevents protein chain elongation by inhibiting the peptidyl transferase activity of bacterial ribosome. It specifically binds to A2451& A2452 residues in the 23S r RNA of 50S ribosomal unit, preventing polypeptide formation. It directly interferes substrate binding . To know more please donot bother to visit the following links:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chloramphenicol
http://www.patient.co.uk/medicine/Chloramphenicol-eye-preparations.htm http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC357302/
http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00446
http://amrls.cvm.msu.edu/pharmacology/antimicrobials/antibiotics-of-veterinary-importance/chloramphenicol
Fig: Mode of action

3). Chloramphenicol : Chloramphenicol is considered as pro typical broad spectrum antibiotics alongside tetracycline & is effective against a wide variety of Gram positive & Gram negative bacteria, most anaerobic microorganisms.
Mechanism of Action:
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antibiotic that stops bacterial growth by inhibiting protein synthesis. It prevents protein chain elongation by inhibiting the peptidyl transferase activity of bacterial ribosome. It specifically binds to A2451& A2452 residues in the 23S r RNA of 50S ribosomal unit, preventing polypeptide formation. It directly interferes substrate binding . To know more please donot bother to visit the following links:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chloramphenicol
http://www.patient.co.uk/medicine/Chloramphenicol-eye-preparations.htm http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC357302/
http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00446
http://amrls.cvm.msu.edu/pharmacology/antimicrobials/antibiotics-of-veterinary-importance/chloramphenicol
Comments