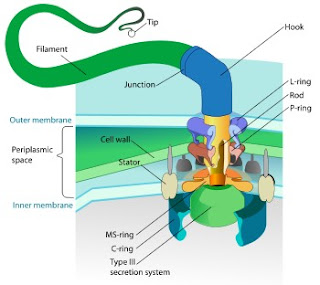
MICROBIAL METABOLISM CONTD...

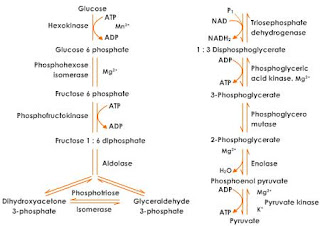
GLYCOLYSIS: Steps: The Embden-Meyerhof or glycolytic pathway is undoubtedly the most common pathway for glucose degradation to pyruvate in stage two of catabolism. It is found in all major groups of microorganisms and functions in the presence or absence of O2. Glycolysis [Greek glyco, sweet, and lysis, a loosening] is located in the cytoplasmic matrix of procaryotes and eucaryotes. The pathway as a whole may be divided into two parts. In the initial six-carbon stage, glucose is phosphorylated twice and eventually converted to fructose 1,6- bisphosphate. Other sugars are often fed into the pathway by conversion to glucose 6-phosphate or fructose 6-phosphate. This preliminary stage does not yield energy; in fact, two ATP molecules are expended for each glucose. These initial steps “prime the pump” by adding phosphates to each end of the sugar. The phosphates will soon be used to make ATP. The three-carbon stage of glycolysis begins when the ...